
This test was transcribed from a wartime original donated to us by our friend Howard Lawson of Jacksonville, Florida.
Use the toggle bar below each question to read the answers.
Because the test was not graded and no answer key was present, we have asked volunteers to proof the information below.
FINAL EXAMINATION FOR RADIO EQUIPMENT ON B-17E (F).
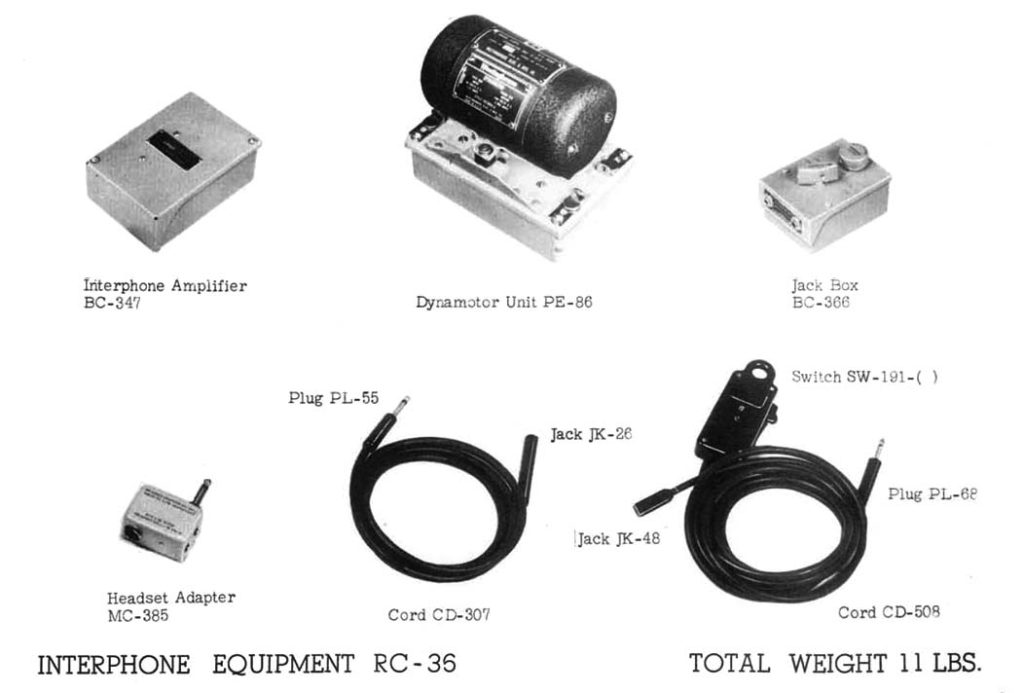

GROUP I * * INTERPHONE EQUIPMENT RC-36
1. In the B-17 there are:
(a) 5 interphone jackbox stations.
(b) 9 interphone jackbox stations.
(c) 11 interphone jackbox stations.
(d) 7 interphone jackbox stations.
(b) 9 interphone jackbox stations.
2. The volume on the INTER and CALL positions of the jackbox
(a) cannot be controlled.
(b) is controlled only by the pilot.
(c) is usually adjusted to the highest level.
(d) is adjusted to the listeners' comfort by turning the control knob.
(a) cannot be controlled.
3. The CALL position is used
(a) only to call the radio range.
(b) for communication between the pilot and bombardier.
(c) to call other stations whose selector switch may not be on the INTER position.
(d) only for intraplane communications.
(c) to call other stations whose selector switch may not be on the INTER position.
4. The LIAISON position is used
(a) only by the pilot.
(b) only by the radio operator.
(c) for transmission and reception with the liaison set.
(d) only on pursuit type planes.
(c) for transmission and reception with the liaison set.
5. The COMMAND position on the interphone jackbox
(a) will key the command transmitter and monitor the command receiver.
(b) is seldom used.
(c) will key the liaison transmitter.
(d) can be used to key any transmitter on the B-17E.
a) will key the command transmitter and monitor the command receiver.
6. The COMPASS position on the interphone jackbox is
(a) never used by anyone but the navigator.
(b) used by all crew members who desire to listen to the radio compass provided it is turned on.
(c) used for interphone communications between crew members.
(d) used in conjunction with the drift meter.
(b) used by all crew members who desire to listen to the radio compass provided it is turned on.
7. The INTER position on the interphone jackbox is used
(a) for communication between the crew members who have their selector switch on the INTER position.
(b) to monitor the command position.
(c) to monitor all positions in the ship.
(d) to carry on interphone communication with a crew member who has his selector on COMMAND position.
(a) for communication between the crew members who have their selector switch on the INTER position.
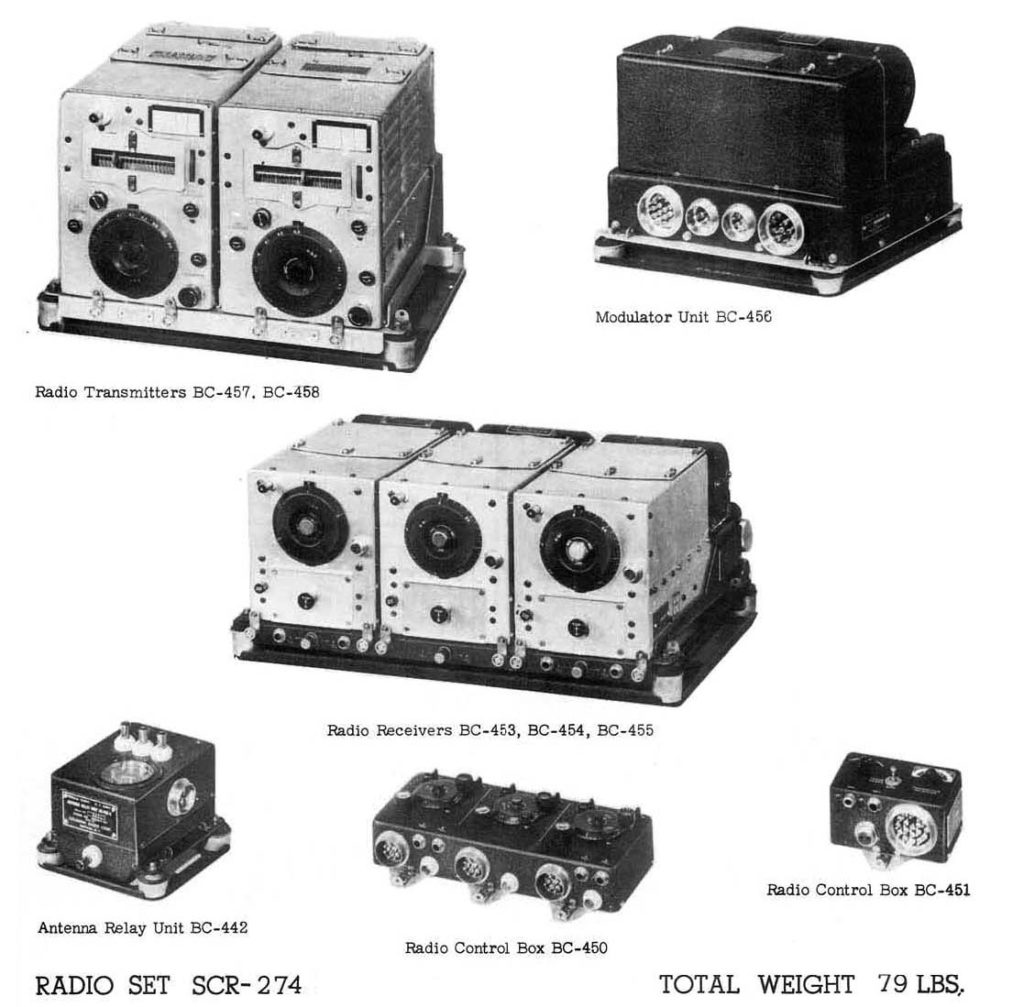

GROUP II * * NEW TYPE COMMAND SET (SCR-274-N)
8. The remote controls for this set are
(a) in the radio compartment.
(b) in the pilot's compartment.
(c) in the tail section.
(d) mounted on the roof on the plane in the navigator's compartment.
(b) in the pilot's compartment.
9. This set contains
(a) 1 transmitter and 3 receivers.
(b) 3 receivers and two transmitters.
(c) 1 transmitter and 1 receiver.
(d) 2 receivers and 3 transmitters.
(b) 3 receivers and two transmitters.
10. The transmitter/s is/are
(a) always tuned on the VOICE position.
(b) tuned on CW.
(c) tuned for minimum antenna current.
(d) tuned for maximum plate current regardless of what the reading is.
(b) tuned on CW.
11. The antenna current indicator is located
(a) on the face of the transmitters.
(b) in the radio compartment.
(c) on the instrument panel.
(d) in the navigator's compartment.
(b) in the radio compartment.
12. How many receivers may be monitored simultaneously with this set?
(a) 1.
(b) 2.
(c) 3.
(d) 4.
(c) 3.
13. To receive the output of these receivers through the interphone jackbox the "A-B" switch must be in the
(a) neutral position.
(b) the "A" position.
(c) the AUTO position.
(d) the "B" position.
(b) the "A" position.
14. The transmitter selector switch for the new command set is located
(a) on the receiver.
(b) on the transmitter.
(c) on the transmitter control box.
(d) in the radio compartment.
(c) on the transmitter control box.
15. These receivers obtain their power from
(a) a dynamotor mounted on the rear of each receiver.
(b) the transmitter dynamotor.
(c) the interphone dynamotor.
(d) the liaison dynamotor.
(a) a dynamotor mounted on the rear of each receiver.
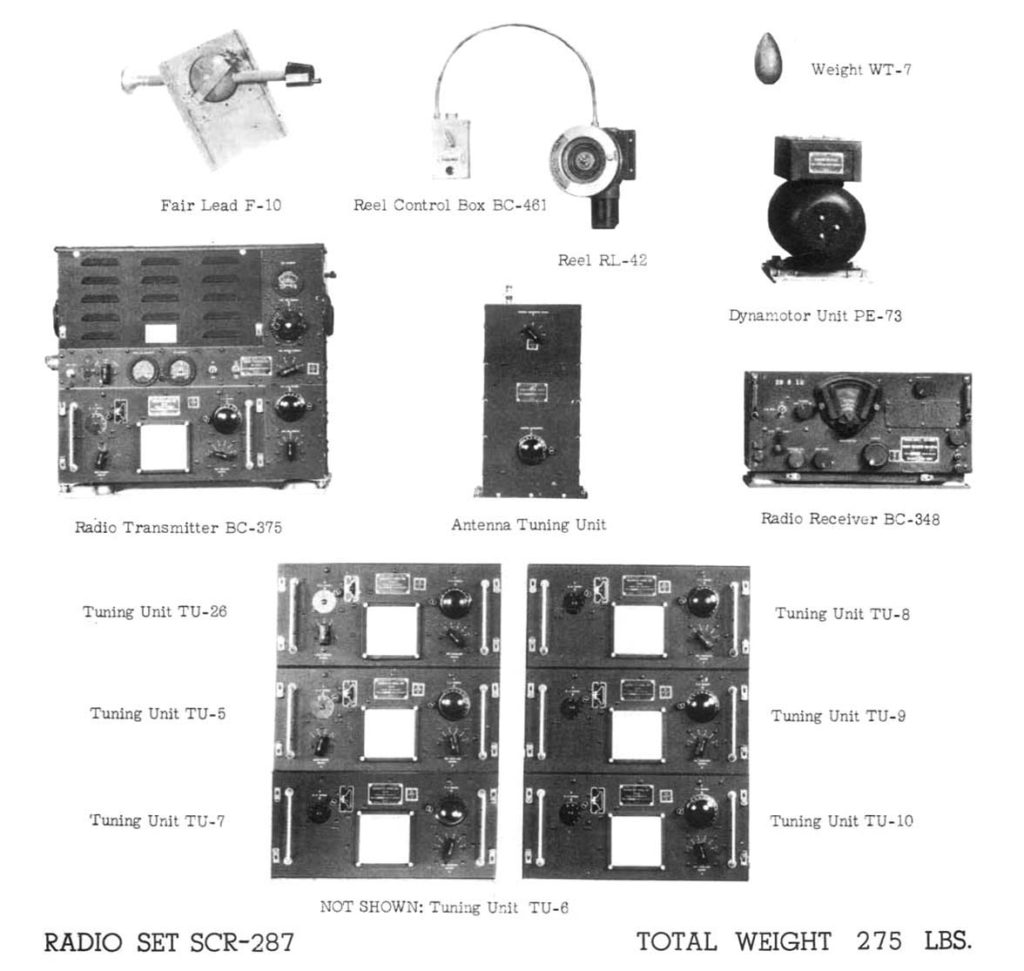
GROUP III * * LIAISON TRANSMITTER.
16. The transmitter is always tuned on
(a) VOICE
(b) TONE
(c) CW.
(d) MCW.
(c) CW.
17. The Master Oscillator dial on this transmitter tuning units is labeled
(a) control A.
(b) control B.
(c) control C.
(d) control D.
(b) control B.
18. The high voltage output of the liaison transmitter dynamotor is approximately
(a) 1,000 volts.
(b) 1,500 volts.
(c) 10,000 volts.
(d) 28 volts.
(a) 1,000 volts. (DC)
19. The liaison transmitter can normally be keyed and modulated from how many jackbox stations?
(a) 2.
(b) 4.
(c) 9.
(d) 6.
(b) 4.
20. The approximate total plate current when the transmitter is completely tuned on CW is
(a) 20 amperes.
(b) 220 amperes.
(c) 220 milliamperes.
(d) 20 milliamperes.
(c) 220 milliamperes.
21. Antenna circuit switch "N" is normally
(a) on #3 position when using the fixed antenna.
(b) on #2 position when using the fixed antenna and #3 position when using the trailing wire antenna.
(c) never used.
(d) remains on #2 at all times.
(b) on #2 position when using the fixed antenna and #3 position when using the trailing wire antenna.
22. The power amplifier tuning control "C" is always tuned for
(a) maximum antenna current.
(b) minimum antenna current.
(c) minimum plate current.
(d) maximum plate current.
(c) minimum plate current.
23. In the top of the dynamotor there is/are
(a) one fuse.
(b) two fuses.
(c) three fuses.
(d) no fuses.
(c) three fuses.
24. The liaison transmitter is located
(a) in the navigator's compartment.
(b) in the radio compartment.
(c) behind the co-pilot's seat in some types of B-17E airplanes.
(d) back of the radio compartment bulkhead.
(b) in the radio compartment.
25. The liaison receiver derives its power from
(a) the ship's batteries.
(b) the ship's inverters.
(c) the magnetos.
(d) a dynamotor within the receiver.
(d) a dynamotor within the receiver.
26. One megacycle is
(a) 1,000 kilocycles.
(b) 10,000 kilocycles.
(c) 1,000,000 kilocycles.
(d) 100 kilocycles.
(a) 1,000 kilocycles.
27. The liaison receiver is controlled
(a) remotely.
(b) locally.
(c) locally and remotely.
(d) by crystals.
(b) locally.
28. Within the transmitter itself there is/are
(a) one fuse.
(b) two fuses.
(c) three fuses.
(d) four fuses.
(a) one fuse.
29. The liaison set (transmitter and receiver) uses the
(a) whip or loop antenna.
(b) wing or loop antenna.
(c) trailing wire or wing antenna.
(d) trailing wire or whip antenna.
(c) trailing wire or wing antenna.
![]()
GROUP IV * * MARKER BEACON RECEIVER
30. The marker beacon operates on a frequency of
(a) 1,000 kilocycles.
(b) 75 megacycles.
(c) 1,000 megacycles.
(d) 75 kilocycles.
(b) 75 megacycles.
31. The marker beacon receiver is turned on by use of the
(a) liaison ON-OFF transmitter switch.
(b) compass transmitter antenna selectors switch.
(c) compass receiver antenna selector switch.
(d) main line switch.
(c) compass receiver antenna selector switch.
32. The marker beacon receiver is reliable up to
(a) 20,000 ft.
(b) 5,000 ft.
(c) 10,000 ft.
(d) 1,000 ft.
(c) 10,000 ft.
GROUP V * * RADIO COMPASS EQUIPMENT (OLD and NEW).
33. What minimum combination of stations and degrees will give the most accurate fix?
(a) 3 stations at least 30 degrees apart.
(b) 4 stations at least 40 degrees apart.
(c) 5 stations at least 30 degrees apart.
(d) 3 stations at least 40 degrees apart.
(a) 3 stations at least 30 degrees apart.
34. The preferred position on the radio compass control box for shooting bearings is
(a) antenna.
(b) compass.
(c) loop.
(d) both.
(b) compass.
35. For homing on the old type compass, the loop should always be in the
(a) 0 degree position.
(b) 90 degree position.
(c) 180 degree position.
(d) 270 degree position.
(a) 0 degree position.
36. When homing with the new type compass and the stations is directly to the rear of the airplane, the pilot's indicator will read
(a) 0 degrees.
(b) 90 degrees.
(c) 180 degrees.
(d) 270 degrees.
(c) 180 degrees.
37. Which of the following types of antenna is/are in use on COMPASS position?
(a) Loop.
(b) Loop and trailing wire.
(c) Loop and whip.
(d) The airplane itself is used for the antenna.
(c) Loop and whip.
38. When homing with the old type compass and the pilot's indicator swings to the left as the ship is turned to the left, the station is
(a) to the left of the airplane.
(b) behind the airplane.
(c) in front of the airplane.
(d) ahead of the airplane and slightly to the right.
(b) behind the airplane.
39. The new type radio compass receiver receives its voltage and current supply from
(a) a dynamotor within the compass receiver.
(b) the ship's inverters.
(c) the ship's generators.
(d) compass control box.
(b) the ship's inverters.
GROUP VI * * FREQUENCY METER.
40. The frequency meter may be used to set the frequency of
(a) a transmitter only.
(b) a receiver only.
(c) both transmitter and receiver.
(d) the marker beacon receiver.
(c) both transmitter and receiver.
41. The division between the LOW and HIGH frequency band in the frequency meter is
(a) 200 KC.
(b) 2,000 KC.
(c) 500 KC.
(d) 10,000 KC.
(b) 2,000 KC.
42. The frequency meter antenna should be connected directly
(a) to the antenna of the transmitter being checked.
(b) to ground.
(c) to the ceiling of the airplane.
(d) should not be connected directly to anything other than the meter itself.
(d) should not be connected directly to anything other than the meter itself.
43. The frequency meter derives its power from
(a) a dynamotor within the frequency meter.
(b) the ship's inverters.
(c) batteries within the frequency meter.
(d) the liaison transmitter dynamotor.
(c) batteries within the frequency meter.
GROUP VII * * FACILITY CHARTS, FREQUENCY AND RADIO RANGES
44. Facility charts are issued each
(a) month.
(b) day.
(c) week.
(d) two months.
(a) month.
45. Facility charts are corrected once each
(a) year.
(b) month.
(c) week.
(d) two months.
(c) week.
46. In an airplane carrying pilot, co-pilot, and radio operator, the required number of facility charts is
(a) 1.
(b) 2.
(c) 3.
(d) 4.
(c) 3.
47. 4595 KC is used by AACS as a
(a) voice frequency.
(b) CW frequency.
(c) tower frequency.
(d) range frequency.
(b) CW frequency.
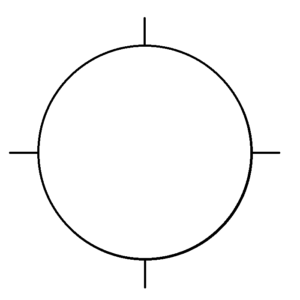
48. On the facility chart, this symbol indicates
(a) Intermediate landing field.
(b) Army first grade landing field.
(c) Commercial airport.
(d) Fan Marker.
(a) Intermediate landing field.
49. One should fly at even thousands plus 500 feet above sea level when flying
(a) off airways east of true north.
(b) off airways west of true north.
(c) on airways flying north.
(d) on airways flying south.
(b) off airways west of true north.
50. A triangle drawn around the symbol of a radio range indicates
(a) station location marker.
(b) fan marker.
(c) an intermediate landing field.
(d) station does not transmit on voice.
(a) station location marker.
WRITTEN PHASE ON ALL SUBJECTS COVERED
51. How many tubes are actually in use for CW transmissions when using the liaison transmitter?
Two.
52. What indication do you get if the 60 ampere fuse in the top of the liaison dynamotor is blown?
The dynamotor will not run.
53. What indication do you get if the 30 ampere fuse in the top of the liaison dynamotor is blown?
The tubes will not burn.
54. What indication do you get if the 1/2 ampere, 1000 volt fuse in the liaison transmitter is blown?
No indication on plate current meter.
55. Explain the use of each position on the antenna circuit switch "N" (2 and 3) on the liaison transmitter.
2 is fixed wire.
3 is trailing wire.
56. How many OFF/ON switches is the liaison transmitter equipped with? Give location of each switch/es.
Two. One on the table and one on the transmitter.
57. Explain the use of the CW oscillator OFF/ON switch on the liaison receiver.
OFF for Voice and ON for CW.
58. What is the purpose of a dynamotor?
Produce voltage for radio equipment.
59. Explain the use of the "A-B" switch on the new type command set.
Switch between audio output (TEL) channels.
60. Name at least three advantages of the new type command set over the old type.
More than one frequency crystal channel.
61. On what frequency does the emergency transmitter SCR-578 (Gibson Girl) operate?
500 kc.
62. Is the antenna needed to transmit with the signal lamp when using the SCR-578?
No.
63. Give two precautions against bodily injuries when using the SCR-578.
64. What signal is transmitted when using the positions: Manual; Auto #1; Auto #2; on the SCR-578?
Manual - CW Message
Auto #1 - 20 second dash SOS
Auto #2 - 20 second dash Automatic Alarm.
65. When using the SCR-578, what antenna length should be used to transmit?
300 ft.
66. Explain the use of the filter switch box with positions: Both; Voice; Range.
Both offers simultaneous Voice and Range listening, while Range provides beacon station signal only and Voice offers voice only.
67. Give external location of command set antenna.
Vertical stabilizer to left wing.
68. Where is the marker beacon antenna receiver located in the B-17E?
Just inside door.
69. What is the use of the marker beacon receiver? Give at least two uses.
Receive 75 megacycle signal used to locate and identify station beacon marker - for markers.
70. Is the length of the marker beacon antenna critical?
Used to locate and identify station.
71. Does the facility chart have an index? If so, where is it?
VEs on the back of the last page - (outside cover)
72. What frequencies should you use for transmitting and receiving when working in AACS station on voice?
Transmitting 4495. Receiving 4220.
73. Why does a radio range station sometimes send out a series of dits?
To notify pilot that a voice transmission is about to be sent.
74. On the radio compass, give two differences between the loop position and the compass position.
Compass position volume is automatic. Compass position gives pilot visual direction to station by automatically moving the visual indicator.
75. Using the new type command set, how would it be possible to have interphone communication if the interphone equipment is inoperative?
From transmitter switched to either #3 or 4 trans.
76. Whose duty is it to see that facility charts in the airplane are always corrected to date and the sufficient number of charts present?
Crew chief.
77. Why isn't the new command set equipped with a Hi/Lo switch?
3 receivers, 2 transmitters.
78. If the dynamotor on the 3-6 MC command receiver is inoperative, what may be done in order to use this receiver, without requiring the dynamotor?
Switch dynamotor with another reciever.
79. Which quadrant of a radio range is true north always in?
N.
80. What is a good indication of a bad microphone?
When you depress mic button and still hear tower.
81. If the tower told you that you were S3 R5, what would they mean?
Strength weak.
82. What are the two types of range stations? Which is the better?
Adcock and loop. Adcock best.
83. Give three differences between the two types of range stations.
Range and voice at same time.
Strong, reliable.
Severing leg.
84. What is the approximate range of the new command transmitter in miles?
25 - 35 miles.
85. Which types of transmission CW; Voice; Tone; can be received at a greater distance?
CW.
86. What is the advantage of the trailing wire antenna?
Greater distance. Cut down static.
87. On the marker beacon receiver, how is a cone of silence distinguished from a fan marker?
Fan marker keyed to certain number.
88. How is the sensitivity of the swinging needle indicator on the old type compass set adjusted?
By knob labelled COMP. From right to increase sensitivity. From left decrease.
89. Which position of the compass set is never used for orientation on a range? Why?
Compass beacon of AVC.
90. Explain briefly the visual homing procedure using the new or automatic type compass set.
From ship so that needle points to zero. Then by keeping needle on o.
91. Explain briefly the aural null homing procedure with old or new type compass set.
Rotate loop to 90° or 270°. Turn plane till null is acquired. Hold course by using gyro. Fly for 3-5 minutes. Rotate loop to new null position. If leading now increased station is right and forward/left and rear.
Zero loop and fly null to station.
92. How is it possible to put the liaison transmitter 'on frequency' without the use of a frequency meter?
Turn to receive and zero beat out.
93. Why is it not necessary to use a frequency meter on the new type command transmitters?
Crystal col.
94. Which antenna/s is/are used on COMPASS position?
Whip and loop.
95. Give the type of volume control in use on each position of the antenna selector switch on the radio compass control box.
Compass = auto volume.
Loop = manual volume.
Antenna = manual volume.
96. In what position should you place your loop antenna when flying the range on LOOP?
90° - 270° null.
97. If you want to work on AACS station on CW, what frequency do you use for transmitting and receiving?
4595 KC.
98. What does AACS stand for?
Army Airways Communication System.
99. What is the difference between a rectifier and an inverter?
Rectifier changes alternating current to direct current.
Inverter changes direct current to alternating current.
100. On a ship with the new type command equipment, how do you turn the interphone equipment on and off?
Master switch.


